Credit Room Management at Banks in Vietnam
Dr. Phung Thai Minh Trang – Dean of the Faculty of Finance – Banking gave an interview on credit room management at banks and forecasted interest rates for the last 6 months of 2022. The interview was published on
According to the State Bank, by June 9, 2022, credit increased by 8.15% compared to the end of 2021, up 17.09% over the same period in 2021, in line with more positive developments of the economy. Previously, as of May 27, the credit growth of the whole system reached 7.75% compared to the end of 2021.
Thus, the credit of the whole economy has continued to grow strongly recently, although many banks have exhausted their growth quotas since the end of the first quarter.
Looking forward to opening the credit room
According to Dr. Phung Thai Minh Trang, Dean of the Faculty of Finance and Banking – Hoa Sen University, the early exit of the room from the end of the first quarter while the State Bank has not yet granted a new limit will not greatly affect the business results of the banks. Bank. Because besides revenue from credit activities, banks have also been developing income from other services.
However, there are some things to keep in mind, that is, in the context of the economy recovering from the pandemic, running out of room can create certain difficulties for businesses in accessing credit. to get back to production quickly. Thereby, indirectly creating pressure on the quality of loans of banks.
The State Bank of Vietnam last year set a credit growth target of 12% and also had a room to loosen the room so that banks can achieve this target. This year, credit growth target is 14%, which is a relatively high growth rate in recent years. Therefore, experts believe that there will be another round of room loosening in the near future.
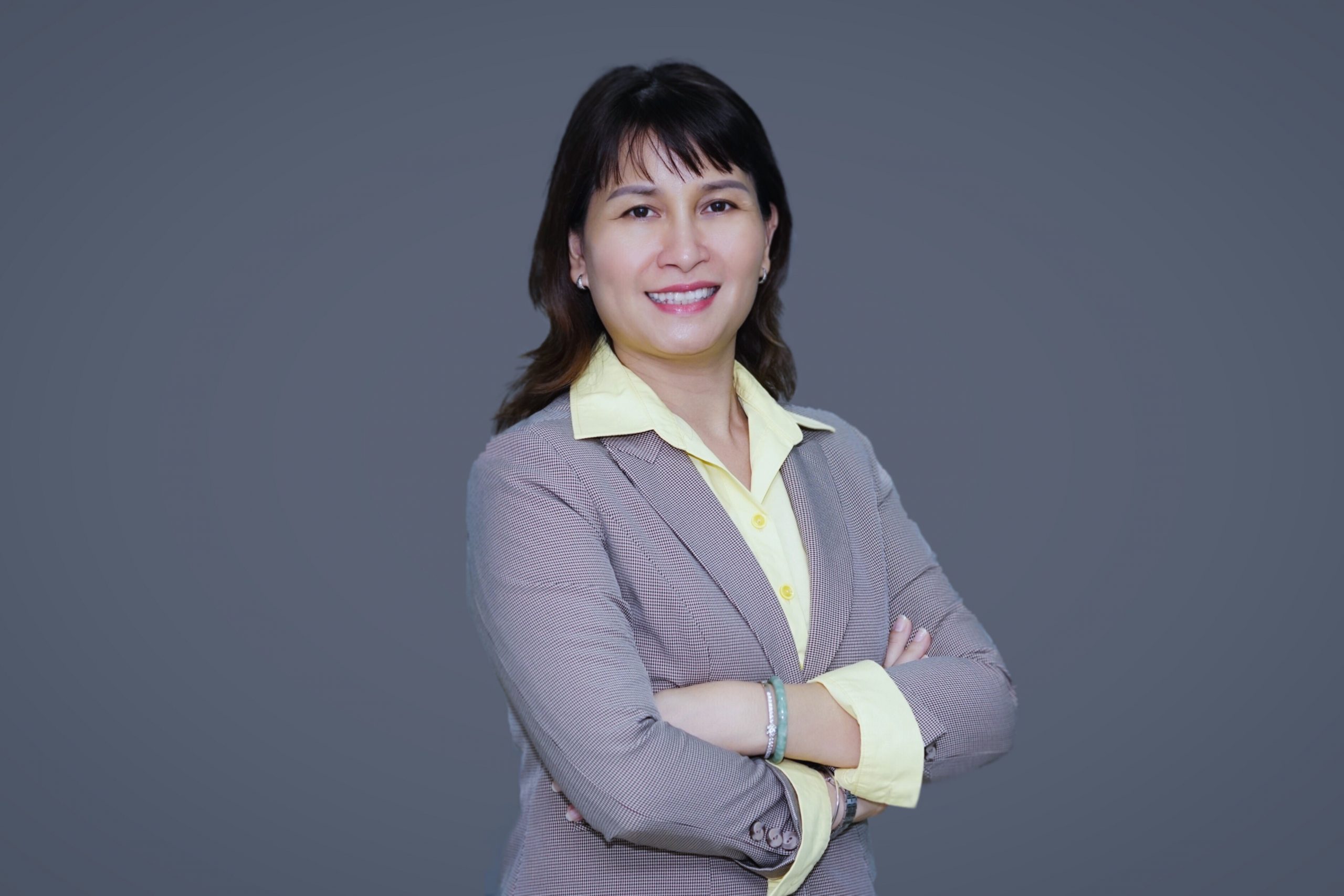

Limited credit room, increased input interest rate, how will banks be affected? – Photo 1.
Dr. Phung Thai Minh Trang
“In 2022, Vietnam’s economy will gradually recover from the COVID-19 pandemic. Businesses need capital to develop production and business. Therefore, it is necessary to propose the State Bank to loosen the credit growth room for banks. However, the loosening of room will have to take place on the principle of ensuring inflation control and macro stability. Whether banks are granted more or less quota will depend on many factors and banks. As observed last year, banks with safe and healthy operations will have an advantage in loosening the room, “- Ms. Trang commented on the situation of credit room in the coming time.
Pressure to increase lending rates
In another development, although the end of the credit room took place in many banks, the deposit interest rate level has been pushed up in the past 2 months. Currently, interest rates up to 7%/year for long terms are no longer rare, even up to 7.5%/year.
Dr. Phung Thai Minh Trang said that the recent increase in interest rates took place not only in deposit rates but also in output interest rates.
Specifically, the increase in input interest rates is mainly due to the fact that banks are anticipating the cash flow out of the real estate and securities markets when these markets are no longer as fertile as before.
The increase in output interest rates is also partly due to the law of supply and demand. Credit as a special commodity. Recently, the supply of this commodity is not as wide as before. That’s why buyers have to be willing to pay more to get access to them.
Besides supply and demand factors, inflation was also a factor that pushed interest rates up over the past time.
In more detail, experts said, when inflation occurs, banks will have to consider actions to protect the interests of depositors, one of which will be to increase deposit interest rates. In order to maintain profit margins, banks will have to consider raising lending interest rates. However, this will have a certain delay and limitation.
On the other hand, the adjustment of interest rates can also affect the borrower’s ability to repay. As a result, the quality of banks’ loan portfolios is also likely to be affected.
In addition, high inflation also has certain effects on the economy such as reduced consumption because of high prices, leading to businesses narrowing production, leading to increased unemployment, reduced credit demand, etc. banks may also be indirectly affected by these adverse macro developments.