CIP Conditions in Air Transport – Responsibilities of buyers and sellers

The CIP condition in air transport (Carriage, Insurance Paid To) – Freight and insurance paid here – is one of the commercial conditions that specifically stipulates the purchase of cargo insurance under certain conditions. Incoterm trade.
Through the article with the topic “Learning about CIP conditions in air transport”, the Faculty of Logistics and International Trade will join readers in decoding the responsibilities and costs between the seller and the buyer as well as determining Place of transfer of risk when transporting goods by air under CIP commercial terms. Let’s start!
Responsibilities of the seller (shipper, exporter)
The role of the seller in CIP terms is as follows:
Prepare goods fully in accordance with the provisions of the Commercial Contract
Complete loading of goods onto domestic transport vehicles (trucks) as well as export customs clearance procedures and bear all customs clearance costs.
The seller must hire an inland transport vehicle to transport the goods to the cargo terminal/airport and bear all risks and losses of the goods before the goods are delivered to the first carrier.
Risk transfer point:

For goods transported by air under CIP conditions, risk will be transferred when the seller fulfills its obligation to deliver the goods to the carrier at the place agreed between the parties, not when delivering the goods to the destination. . Specifically, the seller’s goods obligations end when the goods are safely arranged on the aircraft at the export airport
Regarding cost responsibility, the seller will pay local charges at the export port and air freight from the export airport to the import airport.
And especially, the seller must buy insurance for the shipment to protect the interests of the buyer.
Responsibilities of the buyer (consignee, importer)
According to the provisions of FOB conditions, the buyer is responsible for:
Pay for goods to the seller, sign a transport contract
When the goods arrive at the destination airport, the buyer will pay local charges at the import port. Some basic local charges for imported goods include: cargo handling fee; Delivery Order Fee.
Transporting goods from the destination port airport cargo terminal to the destination, unloading the goods from the inland transport vehicle at the buyer’s warehouse and warehousing.
At the same time, the buyer will carry out import customs clearance procedures, pay import tax and value added tax (if any).
For example:
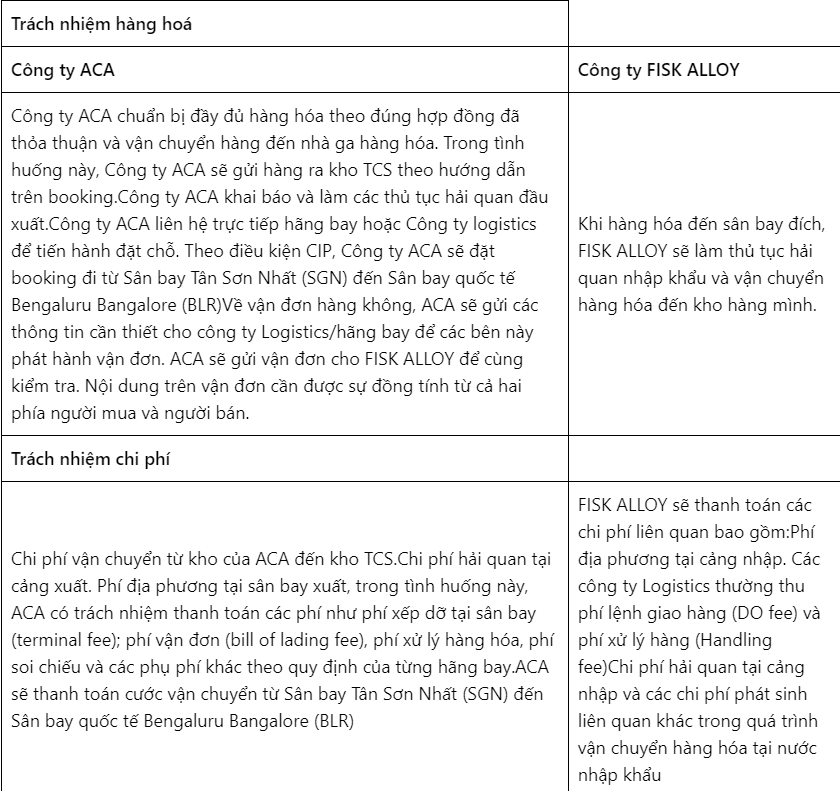
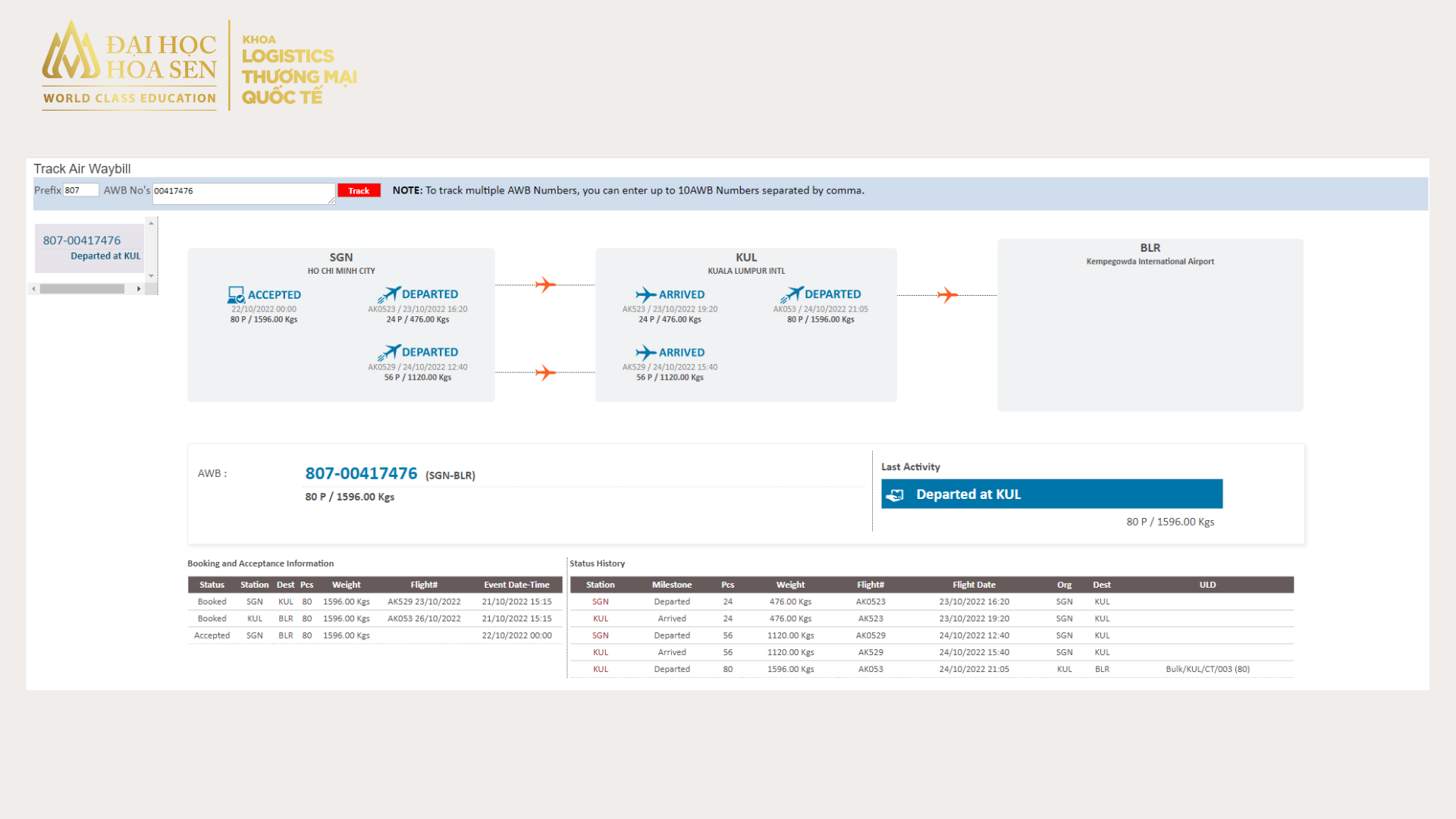
ACA Company exports a consignment of 85 fabric rolls from Tan Son Nhat International Airport (SGN) to Bengaluru Bangalore International Airport Limited – BLR) under CIP terms to FISK ALLOY Company. Each fabric roll has dimensions (156.0 x 30.0 x 30.0 cm) with a total weight of 1584 Kgs. The invoice value of the shipment is 3718 USD.

Below is the allocation of goods responsibilities and costs when ACA Company exports goods to FISK ALLOY Company by air under CIP terms.
Regarding insurance purchase responsibility:
When the seller and buyer sign a sales contract under CIP terms, the seller must have the obligation to buy insurance for the goods so that the buyer can benefit. Some background information about air cargo insurance:
Subjects covered are import and export goods transported by air (excluding goods sent by post).
Scope of insurance: air cargo insurance covers all risks of loss or damage to the subject matter insured (in addition to the insurance exclusions specifically stated in the insurance rules). dangerous).
Sum insured: The sum insured of the insured goods must be the value of the goods declared by the insured and accepted by the insurance company. Normally, the insurance amount is calculated including the price of the goods (C) stated on the sales invoice (or the actual price at the place of shipment if there is no invoice) plus shipping costs (F) and insurance fees ( I). The insured amount may include estimated interest, however this interest must not exceed 10% of the insured value.
Information about insurance for goods transported by air has also ended this article. The Faculty of Logistics – International Trade hopes that readers will find useful and necessary information to expand their knowledge and apply it to their current work.